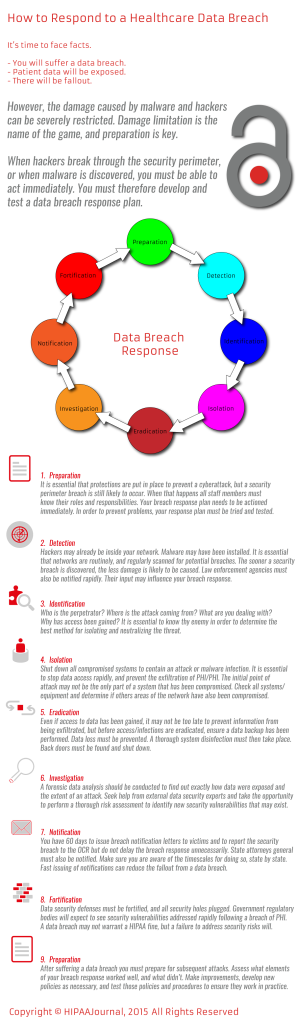
The use of mobile devices in healthcare offers a myriad of benefits; however there are a number of mobile device security risks that must be addressed.
A failure to address mobile device security risks is likely to leave HIPAA-covered entities exposed to cybersecurity attacks and malware infections. A failure to identify and address security risks would also violate HIPAA Rules; the penalties for which can be severe.
The HIPAA Security Rule requires covered entities to implement a number of controls to safeguard the Protected Health Information (PHI) of patients and plan members; however, when HIPAA regulations were first introduced, the use of mobile devices in healthcare was limited. Over the years, use of the devices has grown and they are now an integral component of the provision of healthcare services.
Smartphones are now supplied to healthcare professionals by their employers, Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) schemes have been adopted by many healthcare organizations, and physicians are now using multiple portable devices at work on a daily basis. As use of the devices has grown, so have the risks of data exposure.
Have you Assessed Your Organization’s Mobile Device Security Risks?
HIPAA Rules demand that security measures are employed to protect PHI, although covered entities are given a considerable amount of leeway as to which safeguards are used. Data encryption, for example, is not mandatory, although it is an area that must be addressed. However, there is no flexibility on the risk assessment.
A risk assessment is essential, and the failure to perform regular assessments of all computer systems is a serious HIPAA violation – and one that is punishable with hefty fines. The reason a risk assessment is so important is because the only way to determine if security vulnerabilities exist, is to look for them. A thorough analysis of all computer systems must therefore be conducted, or security holes are likely to persist. Mobile device security risks must also be assessed as part of this vital process.
Once security vulnerabilities have been identified they must be addressed. Organizations do not necessarily have to address all risks immediately, but a plan must be put in place to tackle the most serious security vulnerabilities promptly. A failure to do so could result in a data breach being suffered.
Once vulnerabilities have been identified, there are numerous ways those risks can be mitigated. A number of those strategies have been summarized in the infographic below: